VRVE Formulations Explained
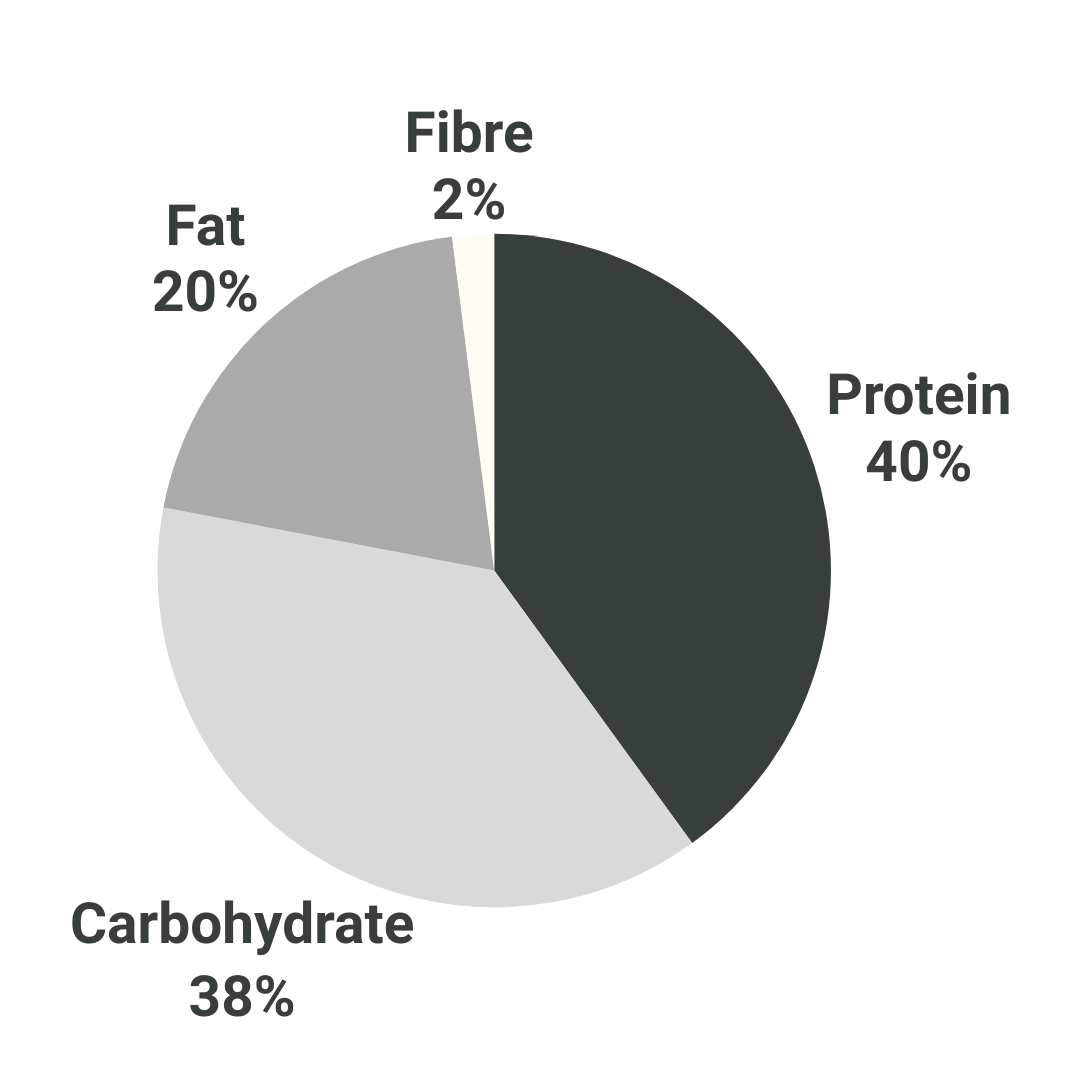
VRVE offers a modern macro split, meaning each meal contains just the right balance of macronutrients (protein, carbohydrate, fat & fibre) to completely nourish your body. Additionally, VRVE also contains all your essential micronutrients (vitamins & minerals).
nutrition info
What's Inside?
Ingredients
Pea Protein Isolate (The Alternative only), Brown Rice Protein (The Alternative only), Grass-fed New Zealand Whey (The Classic only), Bovine Collagen (The Classic only), Sweet Potato Powder, Inulin Fibre, Cocoa (chocolate only), MCT Powder (coconut oil), CLA Powder, Vitamin & Mineral Blend, Sunflower Oil Powder, Xanthan Gum, Stevia, Thaumatin.
Vitamin & Mineral Blend
Calcium Carbonate, Dicalcium Phosphate, Magnesium Carbonate, Zinc Gluconate, Ferric Pyrophosphate, L-ascorbic Acid, Niacinamide, D-alpha-tocopherol, Riboflavin, Pyridoxine Hydrochloride, Thiamin Mononitrate, Retinol Acetate, Folic Acid, Potassium Iodide, Cholecalciferol, Cyanocobalamin.
(Vitamin A, Vitamin C, Vitamin D, Vitamin E, Thiamin, Riboflavin, Niacin, Folate, Vitamin B6, Vitamin B12, Calcium, Iron, Magnesium, Zinc, Iodine, Phosphorus)
Discover our
Macronutrients
Protein
THE CLASSIC (Dairy-based)
Grass Fed New Zealand Whey: Research indicates that milk and milk-derived products, such as whey, from cows allowed to graze on grass year-round offer a more robust nutritional profile when compared to conventionally processed milk products. Grass-fed whey protein is rich in easily absorbable essential amino acids crucial for muscle tissue construction and repair. It's also a source of other vital nutrients like calcium, magnesium, and vitamins B2 and B12. Grass-fed whey boasts the powerful antioxidant glutathione, essential for neutralizing free radicals that can harm cells and the immune system. Furthermore, it can be beneficial for the digestive system as it contains lactoferrin, a protein with antimicrobial properties that can support the growth of healthy gut bacteria. As for taste and texture, the superior grass-fed properties of whey protein enable the blend to deliver a smooth, creamy consistency free from any grittiness or chalkiness.
Collagen: VRVE’s collagen is bovine-derived and is a vital component in our skin, bones, muscles, tendons, and ligaments, playing a crucial role in maintaining the strength, flexibility, and overall health of these structures. Rich in essential amino acids, especially glycine, proline, and hydroxyproline, collagen is pivotal for sustaining the body's connective tissues. Research demonstrates that collagen contributes to skin health and vitality. It also suggests that collagen enhances skin elasticity, moisture retention, and resistance to damage and aging. As we age, our natural collagen production decreases, potentially leading to wrinkles, sagging, and other signs of aging. Incorporating collagen protein powder can help mitigate some of these effects.
THE ALTERNATIVE (Plant-based)
Pea Protein Isolate: Pea protein is rich in essential amino acids, and combined with our premium brown rice protein, makes VRVE’s formulation a complete protein source. This is particularly important for individuals following a vegetarian or vegan diet, as plant-based sources often lack one or more essential amino acids. Pea protein is high in branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs), which are crucial for muscle building and repair. This makes it a suitable choice for individuals engaging in regular physical activity. Furthermore, pea protein is generally well-tolerated and easily digestible. It is a suitable option for individuals with sensitivities to other common protein sources like dairy or soy. It is also hypoallergenic, meaning it is less likely to cause allergic reactions compared to some other protein sources. This makes it suitable for those with allergies or intolerances.
Brown Rice Protein: While brown rice protein is not a complete protein on its own, combined with pea protein it creates a complete amino acid profile. Brown rice protein is also hypoallergenic and suitable for individuals with common allergies or intolerances. It is generally well-tolerated and easy to digest, therefore making it a suitable option for individuals with sensitive stomachs. In addition to it’s protein, brown rice protein contains various nutrients, including fibre, vitamins, and minerals, contributing to a more well-rounded nutritional profile. Additionally, brown rice protein is often considered a sustainable protein source as it is derived from a widely cultivated and accessible crop.
Carbohydrate
The carbohydrates in VRVE are derived from high-quality, raw sweet potato powder. Sweet potatoes in it’s uncooked state offer a low GI (glycemic index), indicating a gradual rise in blood sugar levels and sustained energy. Our finely milled sweet potato powder gives our formulas a natural creamy texture and sweet taste, and ensures a steady release of energy to keep you fueled until your next meal. Additionally, sweet potatoes are rich in vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and fibre, and are naturally free from gluten.
Fat
VRVE’s fat profile consists of medium chain triglycerides (MCTs), conjugated linoleic acid (CLA) and Sunflower Oil Powder, ensuring all essential fatty acids (EFA’s) are included for optimum nutrition.
MCTs: Derived from coconuts, are easily digestible and play a crucial role in VRVE's fat profile, with studies showing their ability to support body fat oxidation (the process where fat is converted to energy). Research suggests that MCTs enhance satiety, supporting healthy weight management. Furthermore, research indicates that consuming MCTs after exercise contributes to faster recovery of muscle function, reduced muscle damage, and diminished inflammation, which can be particularly beneficial for active individuals. MCTs are known to provide quick energy, support cognitive function, and contribute to a feeling of fullness.
CLA: Naturally found in dairy, meat products, and certain vegetable/plant oils, the source used in VRVE formulations is 100% plant-based. Research has proved its capacity to reduce body fat and maintain lean muscle mass, making it an ideal component for a meal replacement. Beyond its weight-loss benefits, CLA has shown potential in lowering inflammation levels and may have a positive impact on insulin sensitivity. This can reduce the risk of chronic diseases like diabetes, heart disease, and cancer.
Sunflower Oil Powder: Derived from the seeds of the sunflower plant (Helianthus annuus) and rich in various compounds like omega-6 fatty acids. Studies suggest that replacing saturated fats with unsaturated fats, such as those found in sunflower oil, may help lower LDL cholesterol levels, reducing the risk of cardiovascular diseases. Furthermore, the presence of vitamin E, an antioxidant, may contribute to its anti-inflammatory properties. Antioxidants help neutralize free radicals in the body, potentially reducing inflammation.
Fibre
The fibre content in VRVE is a mix of naturally occurring fibres from the macronutrients, and added Inulin Fibre.
Inulin Fibre: Inulin serves as a natural prebiotic, promoting the growth and activity of beneficial bacteria in the gut, such as Bifidobacteria. These bacteria play a crucial role in maintaining a healthy digestive system. Research suggests that Inulin can contribute to improved bowel regularity by increasing stool bulk and promoting a softer consistency. This can be particularly beneficial for individuals struggling with constipation. Inulin has also been shown to have a low glycemic index, meaning it has a minimal impact on blood sugar levels. This can be advantageous for individuals with diabetes or those aiming to regulate their blood sugar. Furthermore, Inulin may contribute to a feeling of fullness or satiety, potentially helping with weight management by reducing overall food intake. Inulin may also improve the absorption of certain minerals, such as magnesium and zinc, contributing to overall nutritional status.
Collapsible content
The Finer Details
VRVE formulations offer a comprehensive nutritional profile, providing a minimum of 25% of the Recommended Dietary Intake (RDI) according to the ANZFS (Australia and New Zealand Food Standards). Each serving is loaded with vital vitamins, including Vitamin A, C, D, E, K, and an array of B vitamins such as Thiamine, Riboflavin, Niacin, Folate, B6, and B12. Additionally, these formulations contain essential minerals like calcium, iron, magnesium, zinc, iodine, and phosphorus. These nutrients play pivotal roles in a variety of aspects, ranging from bone health and immune function to energy metabolism and thyroid regulation.
Naturally Sweetened with Stevia & Thaumatin
Stevia, a natural sweetener derived from the leaves of the Stevia rebaudiana plant, and Thaumatin, a natural sweetener originating from the fruit of the katemfe plant, both have a low glycemic index and are calorie-free. Opposed to artificial sweeteners or refined sugar, only a small quantity is needed to attain the desired level of sweetness. This quality aids in reducing ones sugar intake without compromising on taste or flavour.
References
- Moscovici Joubran A, Pierce KM, Garvey N, Shalloo L, O’Callaghan TF. Invited review: A 2020 perspective on pasture-based dairy systems and products. J Dairy Sci. 2021 Jul
1;104(7):7364–82. - Kizhekkedath J. Bioactive Compounds and Milk Peptides for Human Health-A Review. Nov Tech Nutr Food Sci. 2018 May 8;1.
- Hoffman JR, Falvo MJ. Protein – Which is Best? J Sports Sci Med. 2004 Sep 1;3(3):118–30.
- Pizzorno J. Glutathione! Integr Med Clin J. 2014 Feb;13(1):8–12.
- Cava E, Yeat NC, Mittendorfer B. Preserving Healthy Muscle during Weight Loss. Adv Nutr. 2017 May 1;8(3):511–9.
- Clark KL, Sebastianelli W, Flechsenhar KR, Aukermann DF, Meza F, Millard RL, et al. 24-Week study on the use of collagen hydrolysate as a dietary supplement in athletes with activity-related joint pain. Curr Med Res Opin. 2008 May 1;24(5):1485–96.
- Proksch E, Segger D, Degwert J, Schunck M, Zague V, Oesser S. Oral Supplementation of Specific Collagen Peptides Has Beneficial Effects on Human Skin Physiology: A Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study. Skin Pharmacol Physiol. 2013 Aug;27(1):47–55.
- Asserin J, Lati E, Shioya T, Prawitt J. The effect of oral collagen peptide supplementation on skin moisture and the dermal collagen network: evidence from an ex vivo model and randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trials. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2015 Dec;14(4):291–301.
- Paul C, Leser S, Oesser S. Significant Amounts of Functional Collagen Peptides Can Be Incorporated in the Diet While Maintaining Indispensable Amino Acid Balance. Nutrients. 2019 May 15;11(5):1079.
- Babault N, Païzis C, Deley G, Guérin-Deremaux L, Saniez MH, Lefranc-Millot C, et al. Pea proteins oral supplementation promotes muscle thickness gains during resistance training: a double-blind, randomized, Placebo-controlled clinical trial vs. Whey protein. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2015 Jan 21;12:3.
- Pinckaers PJM, Trommelen J, Snijders T, van Loon LJC. The Anabolic Response to
Plant-Based Protein Ingestion. Sports Med. 2021 Sep 1;51(1):59–74. - Mu TH, Tan SS, Xue YL. The amino acid composition, solubility and emulsifying properties of sweet potato protein. Food Chem. 2009 Feb 15;112(4):1002–5.
- Nosaka N, Suzuki Y, Suemitsu H, Kasai M, Kato K, Taguchi M. Medium-chain Triglycerides with Maltodextrin Increase Fat Oxidation during Moderate-intensity Exercise and Extend the Duration of Subsequent High-intensity Exercise. J Oleo Sci. 2018;67(11):1455–62.
- St-Onge MP, Mayrsohn B, O’Keeffe M, Kissileff HR, Choudhury AR, Laferrère B. Impact of medium and long chain triglycerides consumption on appetite and food intake in overweight men. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2014 Oct;68(10):1134–40.
- Nosaka N, Suzuki Y, Nagatoishi A, Kasai M, Wu J, Taguchi M. Effect of ingestion of mediumchain triacylglycerols on moderate- and high-intensity exercise in recreational athletes. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo). 2009 Apr;55(2):120–5.
- Talenezhad N, Mohammadi M, Ramezani-Jolfaie N, Mozaffari-Khosravi H, Salehi-Abargouei A. Effects of l-carnitine supplementation on weight loss and body composition: A systematic review and meta-analysis of 37 randomized controlled clinical trials with dose-response analysis. Clin Nutr ESPEN. 2020 Jun 1;37:9–23.
- Koozehchian MS, Daneshfar A, Fallah E, Agha-Alinejad H, Samadi M, Kaviani M, et al. Effects of nine weeks L-Carnitine supplementation on exercise performance, anaerobic power, and exercise-induced oxidative stress in resistance-trained males. J Exerc Nutr Biochem. 2018 Dec 31;22(4):7–19.
- Abbasi B, Kimiagar M, Sadeghniiat K, Shirazi MM, Hedayati M, Rashidkhani B. The effect of magnesium supplementation on primary insomnia in elderly: A double-blind placebo-controlled clinical trial. J Res Med Sci Off J Isfahan Univ Med Sci. 2012 Dec;17(12):1161–9.
- Siegel JD, Di Palma JA. Medical Treatment of Constipation. Clin Colon Rectal Surg. 2005 May;18(2):76–80.
- Setaro L, Santos-Silva PR, Nakano EY, Sales CH, Nunes N, Greve JM, et al. Magnesium status and the physical performance of volleyball players: effects of magnesium supplementation. J Sports Sci. 2014 Mar 16;32(5):438–45.
- Antonio J, Street C. Glutamine: a potentially useful supplement for athletes. Can J Appl Physiol Rev Can Physiol Appl. 1999 Feb;24(1):1–14.
- Deters BJ, Saleem M. The role of glutamine in supporting gut health and neuropsychiatric factors. Food Sci Hum Wellness. 2021 Mar;10(2):149–54.
- Kim JH, Kim Y, Kim YJ, Park Y. Conjugated Linoleic Acid: Potential Health Benefits as a
Functional Food Ingredient. Annu Rev Food Sci Technol. 2016;7(1):221–44. - Blankson H, Stakkestad JA, Fagertun H, Thom E, Wadstein J, Gudmundsen O. Conjugated Linoleic Acid Reduces Body Fat Mass in Overweight and Obese Humans. J Nutr. 2000 Dec 1;130(12):2943–8.
- Anton SD, Martin CK, Han H, Coulon S, Cefalu WT, Geiselman P, et al. Effects of stevia,
aspartame, and sucrose on food intake, satiety, and postprandial glucose and insulin levels. Appetite. 2010 Aug 1;55(1):37–43. - Ruiz-Ruiz JC, Moguel-Ordoñez YB, Matus-Basto AJ, Segura-Campos MR. Antidiabetic and antioxidant activity of Stevia rebaudiana extracts (Var. Morita) and their incorporation into a potential functional bread. J Food Sci Technol. 2015 Dec;52(12):7894–903.
- Saraiva A, Carrascosa C, Raheem D, Ramos F, Raposo A. Natural Sweeteners: The Relevance of Food Naturalness for Consumers, Food Security Aspects, Sustainability and Health Impacts. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 Sep;17(17):6285.
- Czaja-Bulsa G. Non coeliac gluten sensitivity – A new disease with gluten intolerance. Clin Nutr. 2015 Apr 1;34(2):189–94.
- Babault N, Païzis C, Deley G, Guérin-Deremaux L, Saniez MH, Lefranc-Millot C, et al. Pea proteins oral supplementation promotes muscle thickness gains during resistance training: a double-blind, randomized, Placebo-controlled clinical trial vs. Whey protein. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2015 Jan 21;12(1):3.
- Coleman CD, Kiel JR, Mitola AH, Arterburn LM. Comparative effectiveness of a portioncontrolled meal replacement program for weight loss in adults with and without diabetes/high blood sugar. Nutr Diabetes. 2017 Jul;7(7):e284–e284.
- Franz MJ, Boucher JL, Rutten-Ramos S, VanWormer JJ. Lifestyle Weight-Loss Intervention Outcomes in Overweight and Obese Adults with Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta- Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials. J Acad Nutr Diet. 2015 Sep;115(9):1447–63. 14
- International society of sports nutrition position stand: diets and body composition | Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition | Full Text [Internet]. [cited 2023 Jun 28]. Available from: https://jissn.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12970-017-0174-y
- Joy JM, Lowery RP, Wilson JM, Purpura M, De Souza EO, Wilson SM, et al. The effects of 8 weeks of whey or rice protein supplementation on body composition and exercise
performance. Nutr J. 2013 Jun 20;12(1):86 - Jäger R, Kerksick CM, Campbell BI, Cribb PJ, Wells SD, Skwiat TM, et al. International Society of Sports Nutrition Position Stand: protein and exercise. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2017 Jun 20;14(1):20.
- Sun Y, Ling C, Liu L, Zhang J, Wang J, Tong X, et al. Effects of Whey Protein or Its Hydrolysate Supplements Combined with an Energy-Restricted Diet on Weight Loss: A Randomized Controlled Trial in Older Women. Nutrients. 2022 Nov;14(21):4540.
- Nutrient Reference Values for Australia and New Zealand Including Recommended Dietary Intakes | NHMRC [Internet]. [cited 2023 Jun 29]. Available from:
https://www.nhmrc.gov.au/about-us/publications/nutrient-reference-values-australia-and-new
-zealand-including-recommended-dietary-intakes#block-views-block-file-attachments-contentblock-1 - Clark KL, Sebastianelli W, Flechsenhar KR, Aukermann DF, Meza F, Millard RL, et al. 24-Week study on the use of collagen hydrolysate as a dietary supplement in athletes with activity-related joint pain. Curr Med Res Opin. 2008 May;24(5):1485–96.
Glossary
Calories - the measurement of energy in food
Carbohydrates - sugar molecules and starches that the body transforms into glucose (blood sugar), which is energy for cell functions
CLA - conjugated linoleic acid, a fatty acid that aids metabolic functions
Collagen - a protein that forms the building blocks of muscles, bone, skin and other connective tissue
Fats
- trans- and saturated fats: found in many processed foods and certain foods like red meat - of which over-consumption is likely to compromise health
- monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats: 'healthy fats' that have more benefits than trans- and saturated fats, such as aiding in the absorption of vitamins
GI - glycemic index, a factor to rank the level that carbohydrates raise blood sugar after eating
Gluten - a protein found in certain grains, that holds no essentials nutrition, and can cause autoimmune reactions in people with sensitive intestines
Macronutrients - carbohydrates, fats and proteins, which make up the components required to maintain bodily functions and structures
Micronutrients - also referred to as vitamins and minerals
MCT - medium-chain triglycerides, a type of fat derived from coconuts
Powder - a food powder mixed with water, milk or alternatives to make a meal or supplement shake
Serving - the size of one portion constituting one meal, measured as 70g
